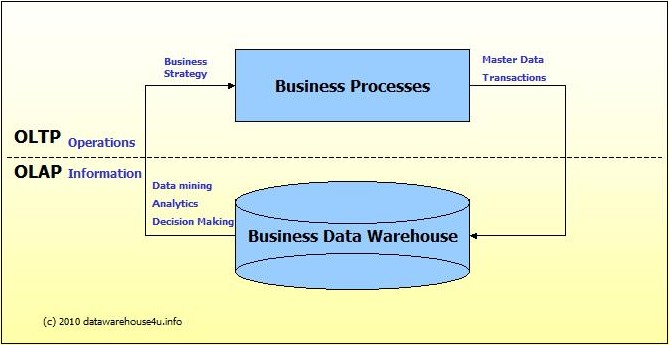
OLTP vs. OLAP
We can divide IT systems into transactional (OLTP) and analytical (OLAP). In general we can assume that OLTP systems provide source data to data warehouses, whereas OLAP systems help to analyze it.
- OLTP (On-line Transaction Processing) is characterized by a large number of short
- OLAP (On-line Analytical Processing) is characterized by
The following table summarizes the major differences between OLTP and OLAP system design.
OLTP System | OLAP System | |
Source of data | Operational data; OLTPs are the original source of the data. | Consolidation data; OLAP data comes from the various OLTP Databases |
Purpose of data | To control and run fundamental business tasks | To help with planning, |
What the data | Reveals a snapshot of ongoing business processes | Multi-dimensional views of various kinds of business activities |
Inserts and Updates | Short and fast inserts and updates initiated by end users | Periodic long-running batch jobs refresh the data |
Queries | Relatively standardized and simple queries Returning relatively few records | Often complex queries involving aggregations |
Processing Speed | Typically very fast | Depends on the amount of data involved; batch data refreshes and complex queries may take many hours; query speed can be improved by creating indexes |
Space Requirements | Can be relatively small if historical data is archived | Larger due to the existence of aggregation structures and history data; requires more indexes than OLTP |
Database Design | Highly normalized with many tables | Typically de-normalized with fewer tables; use of star and/or snowflake schemas |
Backup and Recovery | Backup religiously; operational data is critical to run the business, data loss is likely to entail significant monetary loss and legal liability | Instead of regular backups, some environments may consider simply reloading the OLTP data as a recovery method |


Comments
Post a Comment