Enter the credential manager
Go into system credentials
Add a new credential
(private key of slave node where you want to run the job)
We need a SSH private key credential. I’m not sure the username matters, but I set it to “git” as that is what the login for gitlab uses. I then pointed it to my *private* key on the machine and gave it a description.
Once I had setup the ssh private key, which allows Jenkins to connect to the git host over ssh (i.e. git clone git@server:user/repo.git), I needed to setup API Access for Jenkins to get metadata from GitLab.
In GitLab go to your user profile.
Select “Access Tokens”.
Now make a new token, I gave it a descriptive name and made it expire at the end of the decade (I haven’t investigated the pros/cons of expiration date length yet).
You are then presented with a screen showing the token. Copy it now, as it won’t be accessible again! You can always create a new one if you mess it up though. (FYI I have revoked the token shown above)
Back in Jenkins’s System credentials add a new one of the type GitLab API token. Paste in the API token shown in the last step.
Once the API Access has been setup, we can configure the connection between Jenkins and GitLab. This happens in the Mange Jenkins -> Configure System menu.
Now that our connection between Jenkins and GitLab is setup, we need to create a job. I’ve only worked with freestyle jobs, so if you’re doing a pipeline you’ll be on your own from here on out.
We need to specify the name as “origin”, which will be used by the other sections. For the Refspec we need to input:
+refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/* +refs/merge-requests/*/head:refs/remotes/origin/merge-requests/*
I haven’t completely figured out how this works, but it seems to be correct for my use cases.
For the Branch Specifier we need
origin/${gitlabSourceBranch}
which will be filled in based on the web hook we’ll be setting up next.
For the trigger we want to set it up for changes going in to GitLab.
Finally, in the post build step we need to “Publish build status to GitLab commit”. This enables the feedback and gives us pretty indicators in GitLab.
That’s everything from the Jenkins side. Now we need to setup the GitLab side to trigger the builds. We’ll do this with webhooks, and we’ll need one per Jenkins job.
Now everything should be set! If you push a commit to the repository, you should see the Jenkins job start running. Once the job completes, you should see the status next to the commit in GitLab.
Here’s a few commits with their build result status.
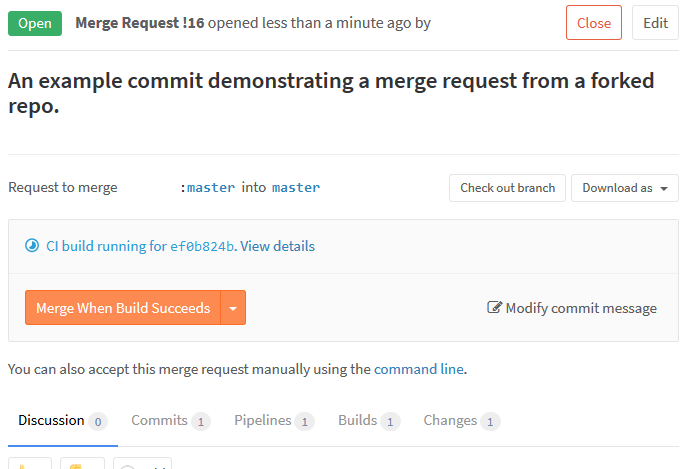
This setup works great for individual commits that are pushed into the repo. However, it also works fine for handling merge requests (despite some of the wording on the Jenkins GitLab Plugin’s readme page). I was able to have merge requests from separate branches in the same repo as well as from forked repos trigger builds and show the resulting status.
Merge request while the build is in progress.























Comments
Post a Comment