What is Kubernetes:
Kubernetes in an open source container management tool
hosted by Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). This is also known as the
enhanced version of Borg which was developed at Google to manage both long
running processes and batch jobs, which was earlier handled by separate systems.
Kubernetes comes with a capability of automating deployment, scaling of
application, and operations of application containers across clusters. It is
capable of creating container centric infrastructure.
Features of Kubernetes
- Continues development, integration and deployment
- Containerized infrastructure
- Application-centric management
- Auto-scalable infrastructure
- Environment consistency across development testing and production
- Loosely coupled infrastructure, where each component can act as a separate unit
- Higher density of resource utilization
- Predictable infrastructure which is going to be created
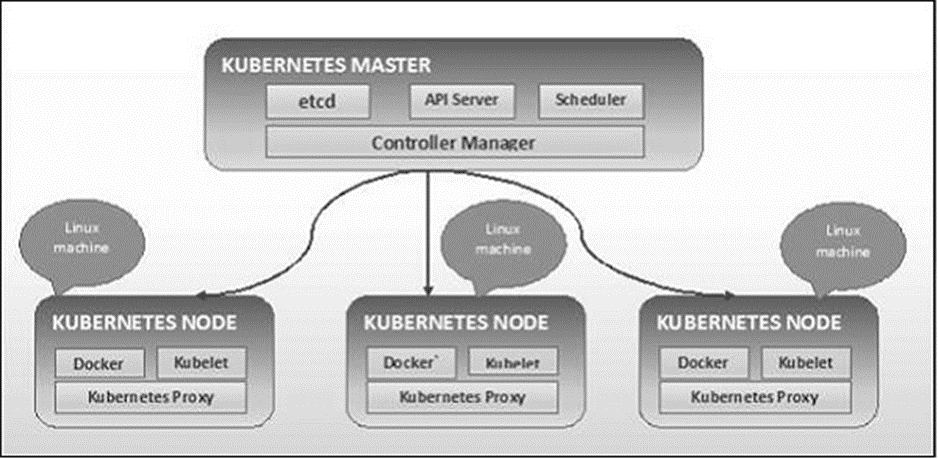
Kubernetes - Cluster Architecture
As seen in the following diagram, Kubernetes follows
client-server architecture. Wherein, we have master installed on one machine
and the node on separate Linux machines.
Kubernetes - Master Machine Components
Following are the components of Kubernetes Master Machine.
etcd
It stores the configuration information which can be used by each of the
nodes in the cluster. It is a high availability key value store that can be
distributed among multiple nodes. It is accessible only by Kubernetes API
server as it may have some sensitive information. It is a distributed key value
Store which is accessible to all.
API Server
Kubernetes is an API server which provides all the operation on cluster
using the API. API server implements an interface, which means different tools
and libraries can readily communicate with it. Kubeconfig is a
package along with the server side tools that can be used for communication. It
exposes Kubernetes API.
Controller Manager
This component is responsible for most of the collectors that regulates
the state of cluster and performs a task. In general, it can be considered as a
daemon which runs in nonterminating loop and is responsible for collecting and
sending information to API server. It works toward getting the shared state of
cluster and then make changes to bring the current status of the server to the
desired state. The key controllers are replication controller, endpoint
controller, namespace controller, and service account controller. The
controller manager runs different kind of controllers to handle nodes,
endpoints, etc.
Scheduler
This is one of the key components of Kubernetes master. It is a service in
master responsible for distributing the workload. It is responsible for
tracking utilization of working load on cluster nodes and then placing the workload
on which resources are available and accept the workload. In other words, this
is the mechanism responsible for allocating pods to available nodes. The
scheduler is responsible for workload utilization and allocating pod to new
node.
Kubernetes - Node Components
Following are the key components of Node server which are necessary to
communicate with Kubernetes master.
Docker
The first requirement of each node is Docker which helps in running the
encapsulated application containers in a relatively isolated but lightweight
operating environment.
Kubelet Service
This is a small service in each node responsible for relaying information
to and from control plane service. It interacts with etcd store to
read configuration details and wright values. This communicates with the master
component to receive commands and work. The kubelet process then
assumes responsibility for maintaining the state of work and the node server.
It manages network rules, port forwarding, etc.
Kubernetes Proxy Service
This is a proxy
service which runs on each node and helps in making services available to the
external host. It helps in forwarding the request to correct containers and is
capable of performing primitive load balancing. It makes sure that the
networking environment is predictable and accessible and at the same time it is
isolated as well. It manages pods on node, volumes, secrets, creating new
containers’ health checkup, etc.
Kubernetes - Master and Node Structure

Comments
Post a Comment